What is Transshipment?
Transportation is one of the most important sectors of international trade. Transportation is the method by which people or goods are moved from one place to another. In today's age, it has become one of the important parts of human life. Transportation costs account for the largest part of costs in a global trade. One of the ways of transporting goods is called transshipment, which we will explain further about this type of transportation. We recommend reading this article to all traders and those interested in the world of trade and commerce.
Today, transportation and business in general are affected by many factors. Sometimes, in the import and export of goods, the goods may not be loaded and transported directly to the destination country. Therefore, traders first transfer their goods to an intermediate country and from there, by changing the means of transportation, they send their goods to the destination country. This method, which is called tranship, is often done to reduce the costs of transportation or bypass the sanctions imposed against the destination country, and is a subset of transit.
Transshipment is increasing for many ports and terminals are trying to identify ways to keep pace with demand. The goal is to find ways to maximize the efficiency of this type of transportation by finding ways to reduce costs and increase productivity.
What is Tranship how is it done?
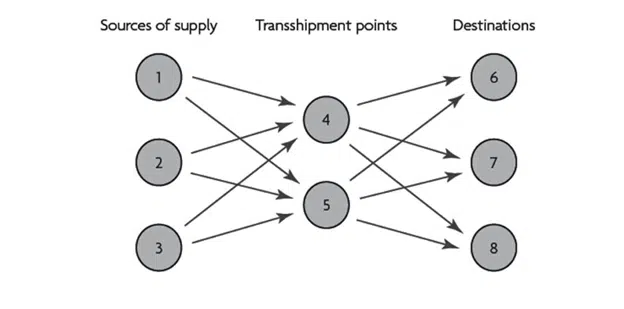
Transhipment means transporting cargo to an intermediate destination and then to the main destination. This type of transportation takes place when there is no direct route to the destination. One of the reasons for doing this is to change the means of transportation during the trip, for example, loads are unloaded from ships and loaded onto planes. Another reason is to merge smaller shipments into a large shipment and vice versa to divide a large shipment into smaller shipments.
International Tranship
Many international transits are carried out in customs areas, so customs checks and duties are avoided, otherwise it will cause delays in efficient transportation. The global transit index has reached 28-30% in recent years. Due to the development of canals and ports, especially in regions with growing economies, the probability of this index reaching 35% is predicted. This method of transportation is normally quite legal and done as part of everyday global trade, but it can be used as illegal entry, smuggling or ash market goods. This transit method is usually done to save the cost of transportation, but it increases the time to reach the destination.
Delay In Transshipment
Delays when sending cargo abroad, due to the longer route, are quite common in such conditions. Due to the nature of transhipment, your shipment will be unloaded and loaded onto another vessel, which will take more time. It may take a week for a port to fully load an incoming ship and another week to load it onto a new ship arriving at its final destination. These long delays can be the result of port congestion and sometimes extend into month-long delays. For this reason, using this method is only recommended if there is no direct transportation route to the destination.
Transshipment Tracking
The best way to track your shipment while using this transit method is to use the online tracking feature of the shipping route. You can go to the website of the shipping company that is responsible for transporting your cargo and enter your waybill number and get information about the time of departure and arrival of the ship. You can also view the other ship that the cargo is carrying for its final destination along with the details of the departure and arrival dates.
Transshipment Centers
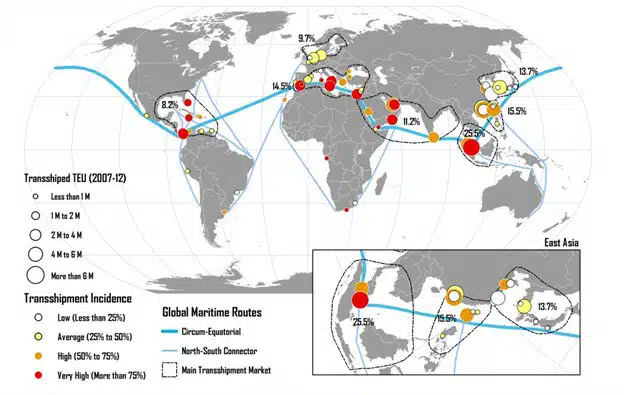
Transshipment often occurs at the intersection of shipping routes and at straits such as the Panama Strait, Suez, and Gibraltar. The map below shows that these centers are located along the main sea route around the equator. These routes are specifically used for Asia-Middle East-Europe trade. Major transhipment hubs usually have a slight maritime deviation from the main shipping lanes, and many of them provide connections or intersections between north-south and east-west shipping lanes.
The degree of activity of a port can be measured by its transhipment rate. The higher the share of the port in the total traffic of the region, the more that port can be considered as a transhipment center. For ports with a lower throughput (less than 25%) this type of transit is an incidental activity, while ports with a throughput above 75% can be considered as net centers (especially if their transportation rate is more than 90%). In the map below, the most important net transportation centers in the world are shown in red.
There are seven major transhipment markets that account for the majority of global transhipment activity. Since this activity is not necessarily tied to a specific port, related hubs compete to receive traffic related to a region or market. This type of transit makes it possible for ports that have limited maritime services due to the smallness of their country's internal areas to have a great connection with global maritime trade.
The Difference Between Bransit And Transshipment
The terms "transit" and "tranship" are often used interchangeably, and their legal definitions can vary by purpose and between jurisdictions. The International Foundation for Customs Operations – the 1974 World Customs Organization International Convention on the Simplification and Harmonization of Customs Procedures (Revised Kyoto Convention) – defines transit as “the customs process by which goods under customs control move from one customs office to another is transported" and defines transit as "a customs process during which goods under customs control are transferred from an imported means of transport to an exporting means of transport in the area of a customs office which is an import and export office".
In layman's terms, transit is the movement of goods through a territory where the goods remain in the original means of transport (for example, a ship, train or aircraft), and transshipment is the carriage of goods through a territory where the goods are transferred from one vehicle to another. The shipment is unloaded and loaded onto another means of transportation.
Shipments that are transported through these two methods, in order to facilitate trade, are usually subject to less regulatory and reporting regulations; Because they are subject to limited tax, safety and security risks for the country they are passing through. However, in order to prevent smuggling and establish more stringent customs controls (e.g. export controls), many legal authorities require that in order to classify shipments by transit or transit, their destination or consignee must be the same destination when they enter the territory. or the recipient is when leaving the territory.
The Future Of This Type Of Transport
In recent years, the global transhipment index has stabilized in the range of 28-30%, which means that it is now considered a broad activity. Therefore, its future growth can be proportional to the global growth of transportation density. But what factors can increase the scale of this type of transit? An important issue is the growing deployment of larger container ships that call at fewer ports, which will lead to greater reliance on transshipment. In addition, the expansion of the Panama Canal will help trans-equatorial maritime services with north-south relations by increasing transhipment dependence. This is balanced by the growth of ports in developing economies such as Latin America and Africa, which can establish more direct services with ports in Asia, Europe and North America.
With greater economies of scale and the rationalization of maritime transport by focusing on selected routes in the deep sea, the global share of this type of transport could reach 35%. Due to geographical considerations, it seems unlikely that the transshipment markets will change. But which ports are the poles of this work in the market? The transit area can have a stable level of activity, but its individual centers are likely to experience stock market fluctuations. The use of transshipment centers is still a decision made by shipping companies and these decisions are made to organize their shipping networks. Such decisions are subject to change if a company reconsiders its asset allocation and business strategy.
Pouyalogistics provides the best transshipment services to you dear customers.
In conclusion, dear ones, you can contact our consultants via email address info@pouyalogistics.com or phone number +9821-88782922 for more information and shipping rates.